Hidden Late Season Intel You Should Pay Attention To
Late Season Deer Hunting | Gut Analysis
By: Weston Schrank, BuckScore® Specialist and Biologist
The original version of this video and blog was posted on Muddy Outdoors and Muddy TV.
This is not your normal late season hunting tips blog, or late season strategy blog. If you are looking for that take a look at a blog we just posted. Instead, this is going to reveal some hidden late season intel that most hunters take the time to look at. Last year, I filmed a weekly video for “Trail Cameras Weekly”, a weekly trail camera tip based video series for Muddy TV that reviewed the deer gut analysis tactic.
Analyzing a Deer’s Gut
Normally, figuring out a deer’s diet is not going to be directly useful for hunting. However, this information is absolutely vital for the late season! I know most hunters are no stranger to taking a doe or two during the late or second gun season of their state (primitive or bonus antlerless season). If so, take advantage of this incredible opportunity!
What Do Deer Eat in The Late Season? | Trail Cameras Weekly “Week 10” – This process offers very valuable intel when it comes to hunting. Figuring out what a deer’s diet consists of regarding the late season food sources on your property, can help you determine where bucks might be patterned.
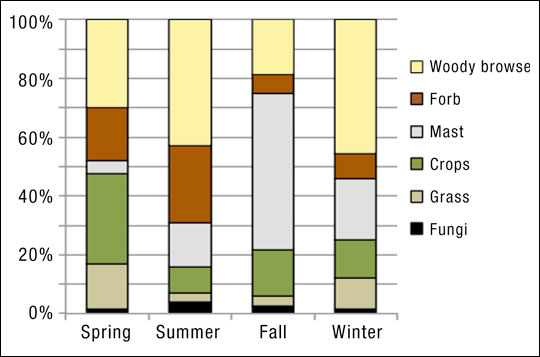
You are essentially trying to figure out what the “green mush” of the stomach contents are and assign percentages of each “type” of food. You will be looking for the following food sources:
- Woody Browse – large high fiber stem and tree bud looking stomach contents. The majority of a deer’s diet will be woody browse which can be confirmed by a lot of fiber strands and broken down stems of plants.
- Forbs – herbaceous plants that can be seen as large green matter. Generally, you will not see a lot of forbs in a deer’s diet in the winter.
- Mast – broken and shattered acorn bits can be confused by corn often, but it will be a significant portion of a deer’s diet in areas with a lot of mast-bearing trees (oaks mostly).
- Crops – this is the one you want to try and focus on. Do you see a lot of corn/beans? In the case of this video, a large portion of the doe’s diet was winter rye or the cover crop on the property.
- Grass – slightly less fibrous plant material that will make up a small portion of a deer’s diet.
The graph below is taken from Nutritional Requirements of White-tailed Deer in Missouri produced by the Extension Department of the University of Missouri.
If you can accurately identify food sources in the deer’s stomach contents you can then assume where the deer is spending the majority of its time. Remember deer will be mainly feeding in the late afternoon and early into the night. If there is a lot of acorns still in the diet, than oak flats may be where you want to spend time hunting. If its corn or another late season food source that can be easily hunted, start putting some late season trail camera setups in and around that food source.
This tactic can turn you onto to an unknown food source on or close by your property. This can allow you to rethink your hunting strategy for the late season just in time to snatch success before the season ends.
Want to Find Out More about this Tactic? Visit the Original blog here!