How to Score Velvet Bucks | Estimating and Scoring Velvet Bucks
Scoring Bucks | How to Score Velvet Bucks
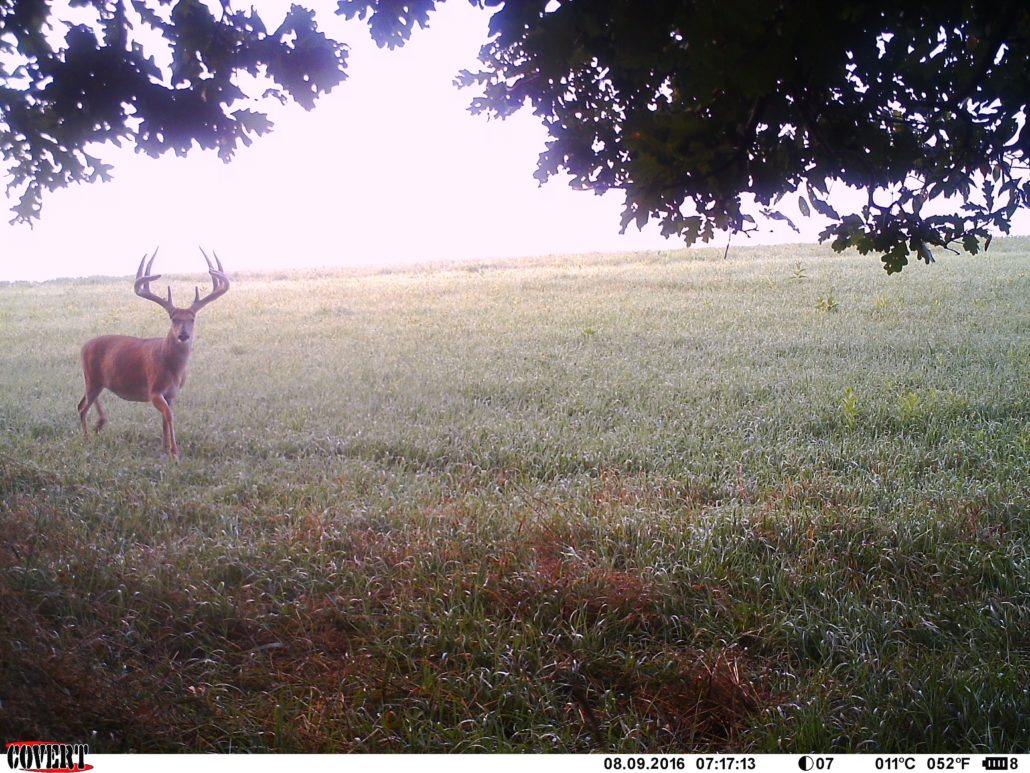
The chance of actually harvesting a velvet buck is greater in some states than others and it’s this rarity of harvesting a velvet buck that is exactly what makes it so special. For others, velvet bucks are just part of the offseason hit-list, gathering, sorting, and strategizing over fuzzy antlered pictures. In either case, whether you are building a hit-list or have a chance at harvesting a velvet buck, the same set of questions apply… how do you go about scoring velvet bucks? How do you estimate a velvet buck’s score from a trail camera picture? How does that score translate into a score for when the buck has hardened antlers? This article will discuss some things to consider when scoring deer in velvet and estimate antler score from velvet bucks.
When do antlers stop growing?
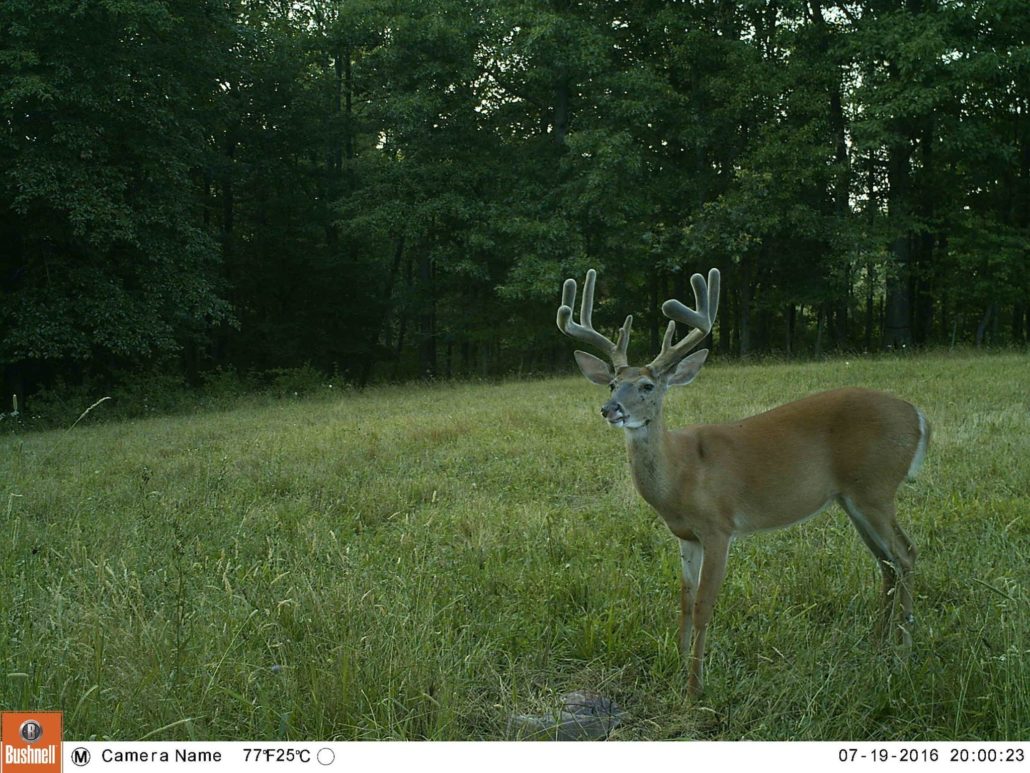
Antlers are an amazing feature on white-tailed deer and the fact that antlers are shed on a yearly basis and grow back makes them that much more special. Antler growth generally begins in late April but depends on several variables including the health of the individual buck. It takes an average of about 120 days for a buck to grow his antlers with antlers growing up to ½ inch per day at their fastest point. But believe it or not, antlers are pretty much done growing by mid to late August and then begin to harden. You’ll know that antlers are done growing when the tips of the tines and main beam start to develop sharp points instead of looking so rounded. But generally speaking, what you see is what you get for antler size by the time August rolls around. This is important to keep in mind when you are scrolling through your trail camera pics before opening day of archery season.
Scoring Velvet Antlers
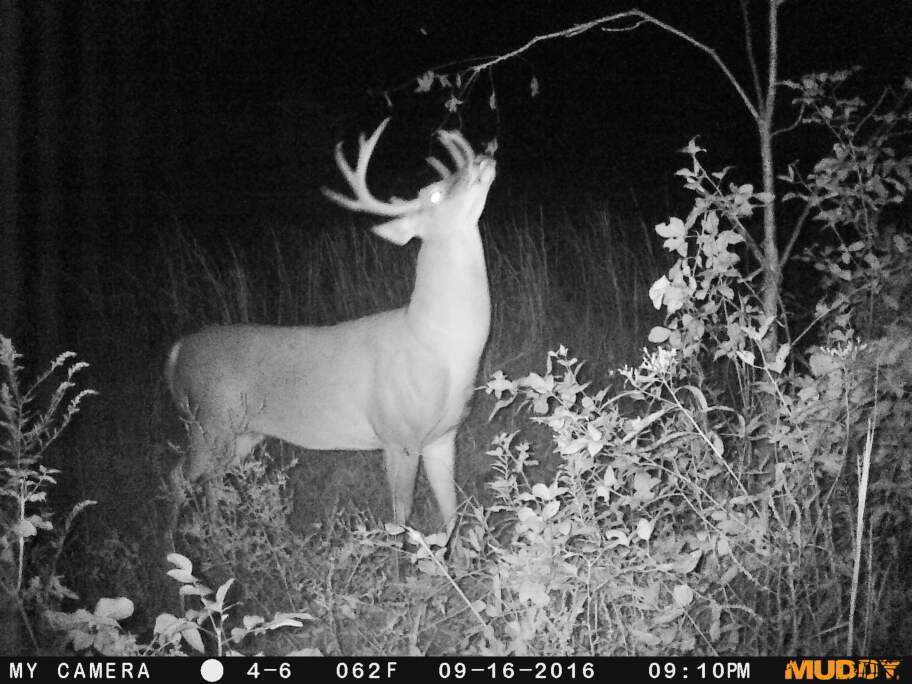
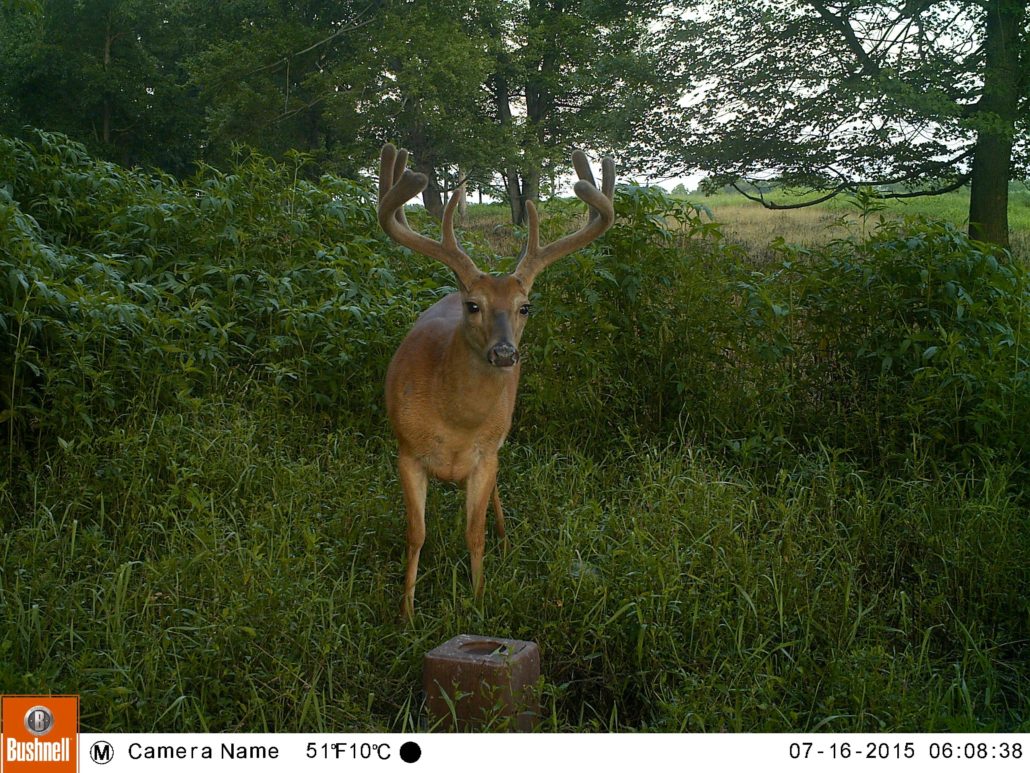
Velvet antlers produce two challenges when trying to estimate their size. First, there is the challenge of estimating what the buck would score after it sheds its velvet. The second challenge is going about scoring and entering your velvet buck in the record books if it is big enough.
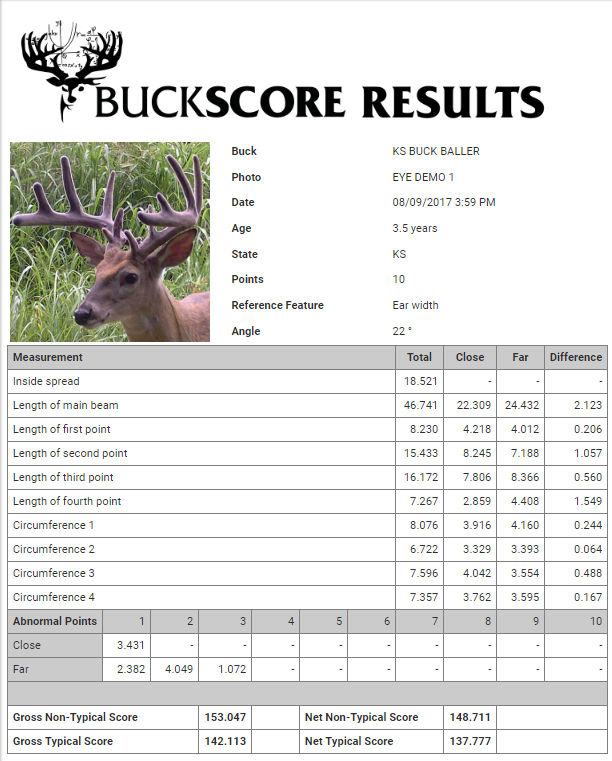
Estimating the score of a velvet buck can be difficult for several reasons. Obviously, antler score is higher when velvet is present but there isn’t much good research out there showing the percent decrease in antler score after velvet is removed. The one exception is the research that BuckScore was developed from, as a reduction value to apply in measurements from velvet to hard antler scores. Regardless, it’s important to keep in mind what measurements will be most dramatically impacted by the presence of velvet. Measurements like main beam length and tine length won’t change as much as the circumference measurements will when a buck is still in velvet. If you’re estimating antler score from a velvet buck, it’s smart to be more conservative on circumference scores if you are hoping to get an idea of what a buck will score once he’s shed his velvet.
Scoring your velvet buck is the same as scoring a buck without velvet. All of the measurements you would take for a scoring system used by groups such as the Pope and Young Club or the Boone and Crockett Club are the exact same. The issue comes if you harvested a big enough buck to enter it into one of these two record books as they differ on how they handle velvet bucks. If you are wanting to enter your buck into the Pope and Young Club, then there is no issue with the velvet. The Pope and Young Club will enter velvet bucks with whatever their score is with the velvet on. They don’t have a correction factor and won’t make you remove the velvet first before scoring. However, the Boone and Crockett Club is different. They will not score a buck if it has any velvet present that will affect the overall score. Instead, they will make you remove the velvet before scoring. You may ask yourself why not just enter your velvet buck with the Pope and Young Club if that’s the case? Keep in mind that the Pope and Young Club only accepts animals harvested with archery gear whereas the Boone and Crockett Club will accept bucks harvested by any legal means.
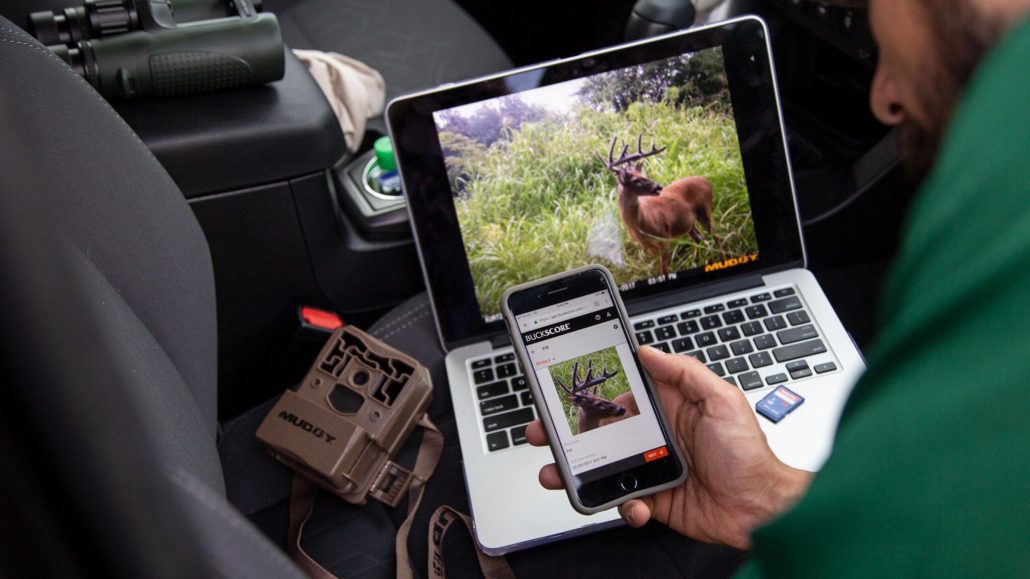
How BuckScore Scores Velvet Bucks
If you are looking to quickly generate a score that applies a factor that relates to the score of a hard antlered buck from a velvet buck picture or harvested buck, BuckScore is your solution. When developed a reduction value was applied and tested, resulting in the ability to accurately estimate the score of a velvet buck.
Judging antler score for velvet bucks can be difficult and you have to manage your expectations of what that buck will actually score once the velvet is gone. It’s easy to get caught up in how big a buck looks with his velvet on but understanding that there will be shrinkage will help you manage your expectations. If you are trying to estimate the velvet buck’s score, use BuckScore to keep your expectations within 3% of his actual score!
Regardless, there’s something special about velvet antlers and having the chance to harvest a buck with velvet is something that doesn’t happen often. Make sure to keep these things in mind regardless of whether you are looking through trail camera pics or are lucky enough to harvest a velvet buck!